 |||
5 minutes
|||
5 minutes
What is Creatine Monohydrate & Its Benefits
Creatine is made in the body and even found in the foods we eat. It helps with short bursts explosive energy and power, say in instances such as fight/flight response or when you workout.
Creatine monohydrate is one of the most researched & commercially available forms of creatine used in supplements.
How does creatine work?
Before Understanding Creatine, which is one of the most well-researched and tested sports nutrition supplements, you need to understand energy production in the body. Every cell needs energy to function. Muscle cells need energy to contract. This energy is in the form of a molecule called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). Energy is produced when one of the phosphate groups is removed from the ATP molecule. Once the one phosphate group is removed, only two remain. The molecule is now called ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate). This “recycling” process requires energy and the replacement of the third phosphate.
This brings us back to Creatine. Creatine can support energy production by supporting ATP regeneration.
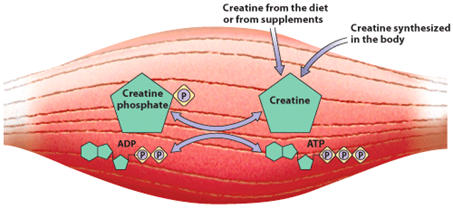
Creatine Monohydrate Benefits?
Our bodies make around a gram of Creatine each day from the Amino Acids Arginine, Glycine, and Methionine. The process starts in the kidneys and is completed in the liver. The body uses these three Amino Acids to synthesize Creatine, which is then stored in skeletal muscle as Creatine Phosphate and used for energy.
If we eat a well-balanced diet and have no dietary restrictions or limitations, we could be consuming upwards of another gram or more a day from sources such as Poultry, Fish, Meat. A typical serving of Chicken or Meat contains around 200 milligrams of Crebatine. Vegetarians can consume a variety of protein sources throughout the day to get the recommended amounts of Amino Acids that the body needs to make Creatine.
Arginine is found in Peanuts, Walnuts, Coconuts, Soybeans, Chickpeas, and Oats.
Glycine is found in Spinach, Soy and Sesame Seeds.
Methionine is found in Brazil Nuts, Oats, and Sunflower Seeds.
Taking creatine supplementation is one convenient way of increasing muscle creatine stores.
Creatine may support strength, power, performance, recovery, and muscle building when taken over time with regular resistance exercise.
So, what does this all mean? Taking Creatine daily (training and non-training days) over time combined with high-intensity activities helps support performance, muscle strength and power.
Creatine Supplementation: Who needs it, what form, and how much?
As you now know that our body makes creatine. Typically, sedentary adults will not need creatine supplementation. However, people who are active, work out regularly or are interested athletic performance, taking creatine supplementation may be beneficial. Creatine may support strength, power, performance, recovery, and muscle building when taken over time with regular resistance exercise.
How to Use Creatine
Typically taking about 3-5g of Creatine a day (both training and non-training days) over time (at least a month) combined with high-intensity activities helps support performance and muscle recovery, with regular resistance training. As such, Creatine can support athletes whose sport requires strength, power and explosive movements.
Some Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Creatine Supplementation.
Q. Is creatine loading necessary?
A. As Creatine works chronically over time and not acutely, loading Creatine is simply not necessary. Once muscle Creatine levels are maxed, you are not going increase levels further.
Q. What form of creatine to choose?
A. Creatine Monohydrate. It is the most researched form of creatine.
Q. How much creatine to take?
A. Typically, 3-5 grams of creatine taken daily over a period of time will help with maximizing muscle creatine store.
Q. When is the Best Time to Take Creatine Monohydrate?
A. Creatine does not work acutely, means the effect is not seen immediately. So, time of day does not matter, what matters is that you take it consistently over a period of time.
There are many myths such as Creatine makes females bulk up. Creatine increases water retention. Creatine causes cramping. Creatine causes dehydration. The fact is that creatine is one of the most researched sports nutrition ingredients.
History of creatine supplementation
1993 was the year that forever changed bodybuilding and sports nutrition. It was the year the first commercial Creatine supplements hit the market. And it was as if the Holy Grail was found. The Holy Grail of supplements if you will. It was expensive. It wasn’t uncommon for a 150-gram bottle (a 30-day supply) to sell for well over $100 US. And you had to completely change your meal planning, your training, your work, your school, your social life, your sleep, essentially your life to use it “properly.” You needed to “load it”. Five 5-gram servings every day for 10 days. We watched the clock all day anxiously waiting for our next spoon of this sacred white powder. You couldn’t use Caffeine as it was believed to counteract the Creatine. We walked around for weeks with pounding headaches from stopping our pot-of-coffee-a-day habits abruptly. We weighed ourselves obsessively waiting for that first gram of new weight to appear that we were promised. And every workout felt like our first again as we waited for the first strength gains to materialize like the test subjects were reporting in all the bodybuilding magazines, we read religiously in-between sets of squats and bench presses.
Take Home Message
A few final things in respect to Creatine to consider? As Creatine works chronically over time and not acutely, loading Creatine is not necessary. Once muscle Creatine levels are maxed, you are not going significantly increase levels further. As such, you don’t need to consume large amounts of sugar or anything else to “increase absorption.” And time of day for consumption is less important as well against consistency so you can consume whenever is most convenient for you. Recommend taking Creatine on training and non-training days again whenever it’s convenient for you. And no you don’t need to avoid Caffeine. Creatine can be added into anything you enjoy eating or drinking.
So, if your goals include anything around strength, power, or explosiveness, why would you not want to be using this tool in your performance toolbox?
